Communication Security
The communication is based on Windows Communication Foundation (WCF).
To configure security, you use behaviors and bindings for your WCF service. Bindings and behaviors allow you to configure transfer security, authentication, authorization, impersonation, and delegation as well as auditing and logging

Figure 1, Bindings
With transfer security is the means by which WCF secures messages over the network. WCF gives you two options to implement transfer security: transport security and message security. Transport security secures the entire communication channel (e.g., by using SSL), while message security secures each message individually.
Transport Security
When using transport security, the user credentials and claims are passed using the transport layer. In other words, user credentials are transport-dependent, which allows fewer authentication options compared to message security. Each transport protocol (TCP, IPC, MSMQ, or HTTP) has its own mechanism for passing credentials and handling message protection. The most common approach for this is to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for encrypting and signing the contents of the packets sent over Secure HTTP (HTTPS).
Transport security is used to provide point-to-point security between the two endpoints (service and client). If there are intermediary systems between the client and the service, each intermediate point must forward the message over a new SSL connection.
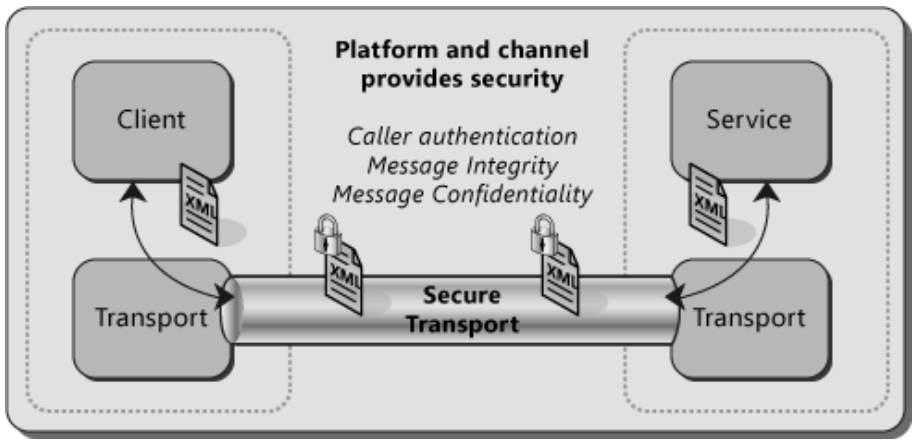
Figure 2, Transport security
Use transport security for the following scenarios:
- You are sending a message directly from your application to a WCF service and the message will not be routed through intermediate systems.
- You have both the service and the client in an intranet.
Using transport security has the following advantages:
- It provides interoperability, meaning that communicating parties do not need to understand the WS-Security specification.
- It may result in better performance.
- Hardware accelerators can be used to further improve performance.
Using transport security has the following disadvantages:
- Because security is applied on a point-to-point basis, there is no provision for multiple hops or routing through intermediate application nodes.
- It supports a limited set of credentials and claims compared to message security.
- It is transport-dependent upon the underlying platform, transport mechanism, and security service provider such as NTLM or Kerberos.
Message Security
When using message security, the user credentials and claims are encapsulated in every message using the WS-Security specification to secure messages. This option gives the most flexibility from an authentication perspective. You can use any type of security credentials you want, largely independent of transport, as long as both the client and the service agree
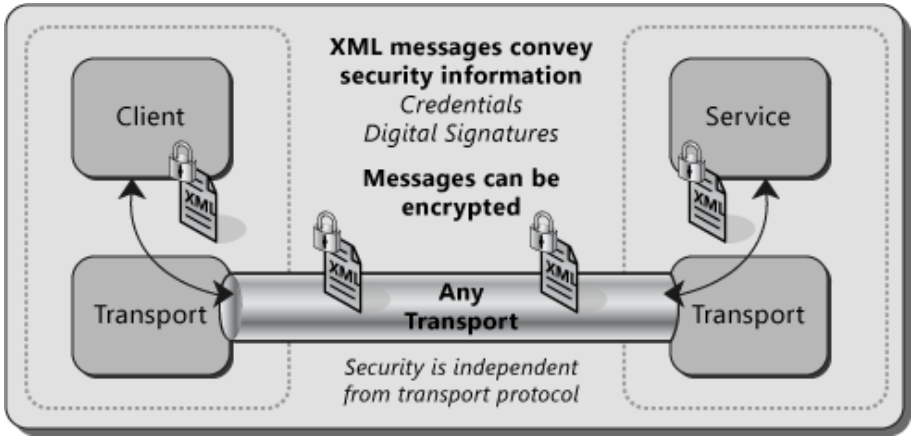
Figuire 3, Message security
Use message security for the following scenarios:
- You are sending a message to a WCF service, and the message is likely to be forwarded to other WCF services or may be routed through intermediate systems.
- Your WCF clients are accessing the WCF service over the Internet, it is possible that other intermediate systems may be used in between, and security is your top consideration.
Using message security has following advantages:
- It provides end-to-end security. Because message security directly encrypts and signs the message, having intermediaries does not break the security.
- It allows partial or selective message encryption and signing, thus improving overall application performance.
- Message security is transport-independent and can be used with any transport protocol.
- It supports a wide set of credentials and claims, including issue token, which enables federated security.
Using message security has following disadvantages:
- This option may reduce performance compared to transport security because each individual message is encrypted and signed.
- It does not support interoperability with older ASP.NET Web Services (ASMX) clients because it requires both the client and service to support WS-Security specifications.
See also WCF